Introduction
Last updated: 8 August 2025
Release cycle management is a crucial aspect of software development that involves planning, scheduling, and controlling the release of software products. This process is designed to ensure the smooth and efficient delivery of new features, enhancements, and bug fixes to end-users while maintaining the stability and reliability of the software.
This document describes the release cycle management within Netaxis and specifies it for the different individual solutions - Fusion, Fusion for BroadWorks and API Orchestrator.
Versioning
The management of releases is categorized into major, minor, and bugfix or patch releases. Each type serves a specific purpose in maintaining and evolving the different software solutions.
Within Netaxis the versioning comes with the following definitions:
Major Releases
Definition: Major releases signify significant milestones in a software product's development. They usually introduce major features, architectural changes, or substantial improvements to the overall functionality.
Purpose: Major releases are often associated with delivering new, groundbreaking features or adapting to changing technological landscapes. They may also involve significant user interface overhauls or major restructuring of the codebase.
Minor Releases
Definition: Minor releases are incremental updates that bring additional features, enhancements, or improvements to existing functionality. They are less disruptive than major releases but still contribute to the overall evolution of the software.
Purpose: Minor releases are geared towards refining and expanding the software without introducing major changes. They may include improvements based on user feedback, performance optimizations, or the addition of smaller features.
Bugfix Releases
Definition: Bugfix releases, also known as maintenance or patch releases, focus on addressing and resolving issues identified in the software. They are essential for maintaining the stability and reliability of the product.
Purpose: Bugfix releases are crucial for delivering timely solutions to software defects, security vulnerabilities, or other issues that may impact the user experience. They are often released as needed, outside the regular update schedule.
Release notation
The version number is expressed as MAJOR.MINOR.PATC and provides a quick understanding of the release's impact.
Example: Suppose the solution is currently at version 2.1.3. In this case:
- Major Release is 2.
- Minor Release is 1.
- Bugfix Release is 3.
Users can interpret this version as a minor release with bugfixes, indicating incremental improvements with a focus on addressing specific issues without introducing major changes. This versioning strategy ensures that users can make informed decisions based on the impact of each release on their systems and workflows.
Fusion Release cycle management
The Netaxis solutions follow a well-structured release cycle management strategy to ensure the software's stability, security, and ongoing improvement.
The figure below shows the release cycle strategy for the Fusion and Fusion for Broadworks solution.
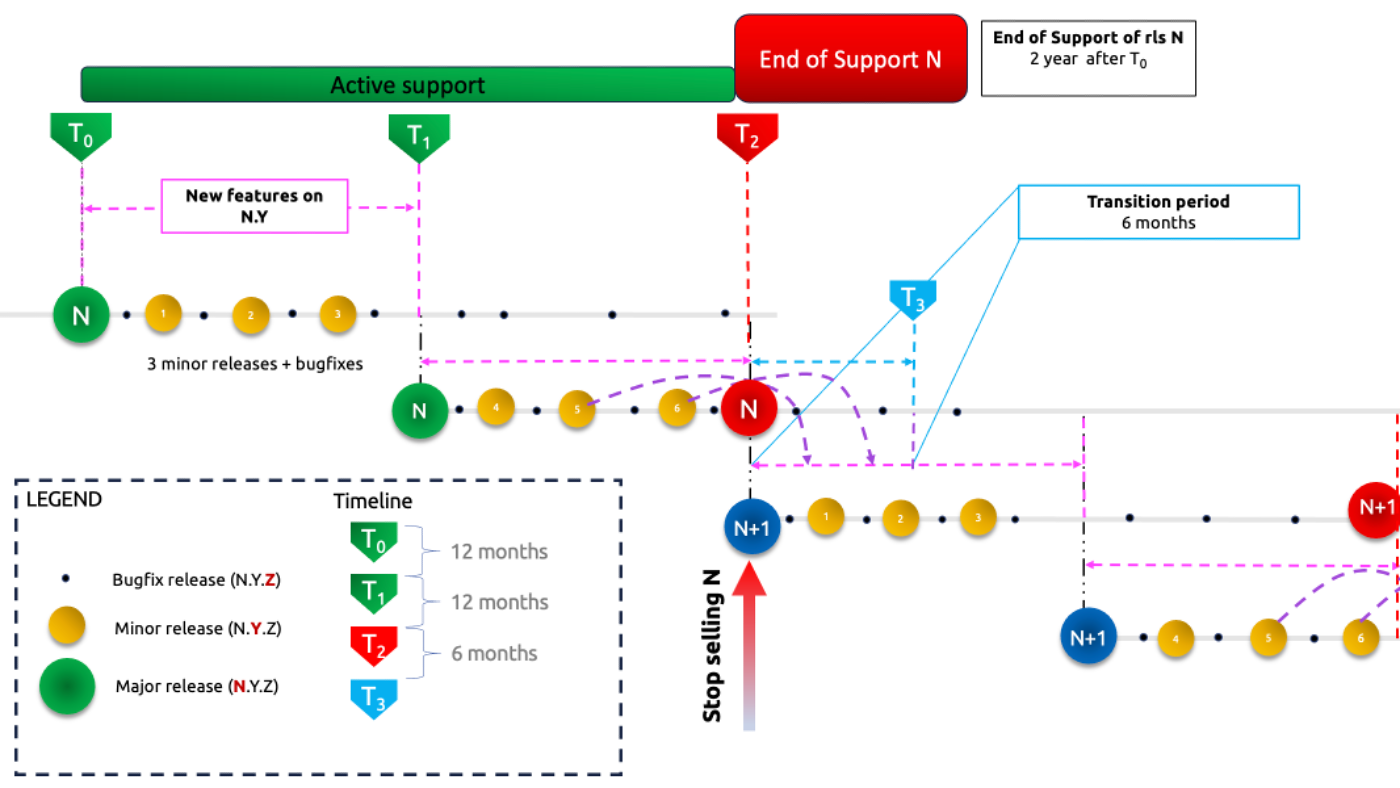
Active Support Period
Fusion and Fusion for BroadWorks (F4B), have an active support period of 2 years. This ensures that users have access to timely updates, bug fixes, and assistance throughout the application's lifecycle.
Once a new MAJOR version of the product has become General Available (GA) the active support period starts.
A first component of this active support is a customer service approach that focuses on identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into problems. The goal of active support is to anticipate customer needs, prevent issues from arising through testing, and provide solutions or assistance before customers realize they have a problem.
This approach involves regularly system testing, analyzing data, and actively engaging with customers to ensure a seamless and satisfactory experience.
Key characteristics of active support include:
Prevention: Prevent problems and disruptions before they occur.
Regular Updates: Keeping customers informed about upcoming changes, improvements, or potential disruptions.
A second component is responding to customer issues or inquiries after they have been raised. It is a traditional approach where customer support teams address problems as they arise and work towards resolving them promptly. This support is typically characterized by resolving customer problems and providing solutions after they have occurred, in a timely and effective manner, identifying the root cause of problems and implementing corrective actions to address them, utilizing ticketing systems to track and manage the customer issues and in severe cases a post-Incident analysis improving to minimize future occurrences.
Bugfix porting
When a bug is found in a minor release Y due to the introduction of a new feature, a patch will be developed and installed in that minor release Y and ported to the next minor release(s) up to the latest minor release in that major release N. When a bug is found in a minor releasy Y which is not linked to a new feature in that release, a patch will be developed and installed in that minor release Y, ported to the previous minor release Y-1 and to the next minor release(s) up to the latest minor release of that release N.
Example: In the release 3.2 is an issue detected which is linked to the introduction of a new feature in that release. A patch release 3.2.1 will be delivered to fix that issue. The fix will also be ported to the next releases 3.3 and 3.4 (if they already exist).
In the release 3.3 is an issue detected which is not linked to a new feature in the release 3.3. A patch release 3.3.1 will be delivered to fix that issue, but the fix will also be ported to a patch release 3.2.3 (which becomes the latest 3.2 release) and to the next releases 3.4 and 3.5 (if they already exist).
Transition period
During the initial 6 months of the active support period of the N+1 release, the support of the latest 2 minor release of the N release will continue. This commitment ensures that users receive ongoing assistance and maintenance for their software environment, fostering a stable and reliable experience. This transition period will also be used to guide the customer to the latest GA release of the solution. In this way, support is guaranteed for the customer for the further product lifecycle.
New features
The Fusion, Fusion for BroadWorks (F4B) development is an ever-evolving process, marked by continuous improvements and feature enhancements. These innovations are systematically introduced through major and minor version releases, strategically outlined in a roadmap. This roadmap serves as a blueprint for the software's development journey, detailing the features to be unveiled in each release.
Major version releases are significant milestones, often accompanied by groundbreaking changes and major feature additions. These releases represent a leap forward in the software's capabilities and are carefully planned to deliver substantial value to users. These features are prominently showcased in the roadmap, providing a clear trajectory for the software's evolution.
On the other hand, minor version releases serve as increments between major updates. While not as sweeping as their major counterparts, minor releases are essential for delivering continuous improvements and smaller feature enhancements. These updates are also meticulously laid out in the roadmap, offering users a glimpse into the ongoing refinement of the software.
It's important to note that the introduction of new features follows a forward-only approach. Once a feature is integrated into a specific minor version release, it is not back-ported to previous minor releases. This approach streamlines the development process, allowing for a focus on advancing the software without the constraints of maintaining feature parity across all minor versions. In the upgrade process it's very important to always upgrade to the latest release of the software and in such way make use of the very latest features of the solution.
Upgrading your system from a release N-1 to the latest release N is a straightforward process that is always supported. However, when considering an upgrade from an older release, N-x, a more nuanced approach is required. This transition requires a case-by-case investigation, taking into account various factors such as the specific release, system architecture, connected applications, and other relevant considerations.
In certain instances, it may be necessary to implement a series of intermediate steps during the upgrade process. This stepwise approach is designed to ensure a smooth and successful transition, addressing potential challenges that may arise due to the age of the release or specific system configurations.
The decision to include intermediate steps in the upgrade process depends on a thorough examination of factors unique to each scenario. Considerations may include the complexity of the upgrade, compatibility issues with connected applications, and potential changes in system architecture. The goal is to identify whether a direct upgrade from release N-x to N is feasible or if a phased approach, involving an interim upgrade to release N-1, is more appropriate.
Ultimately, the upgrade strategy should be tailored to the specific circumstances of your system, taking into account all relevant variables. This ensures a reliable and efficient upgrade process that minimizes potential risks and disruptions while maximizing the benefits of the latest release.
APIO release cycle management
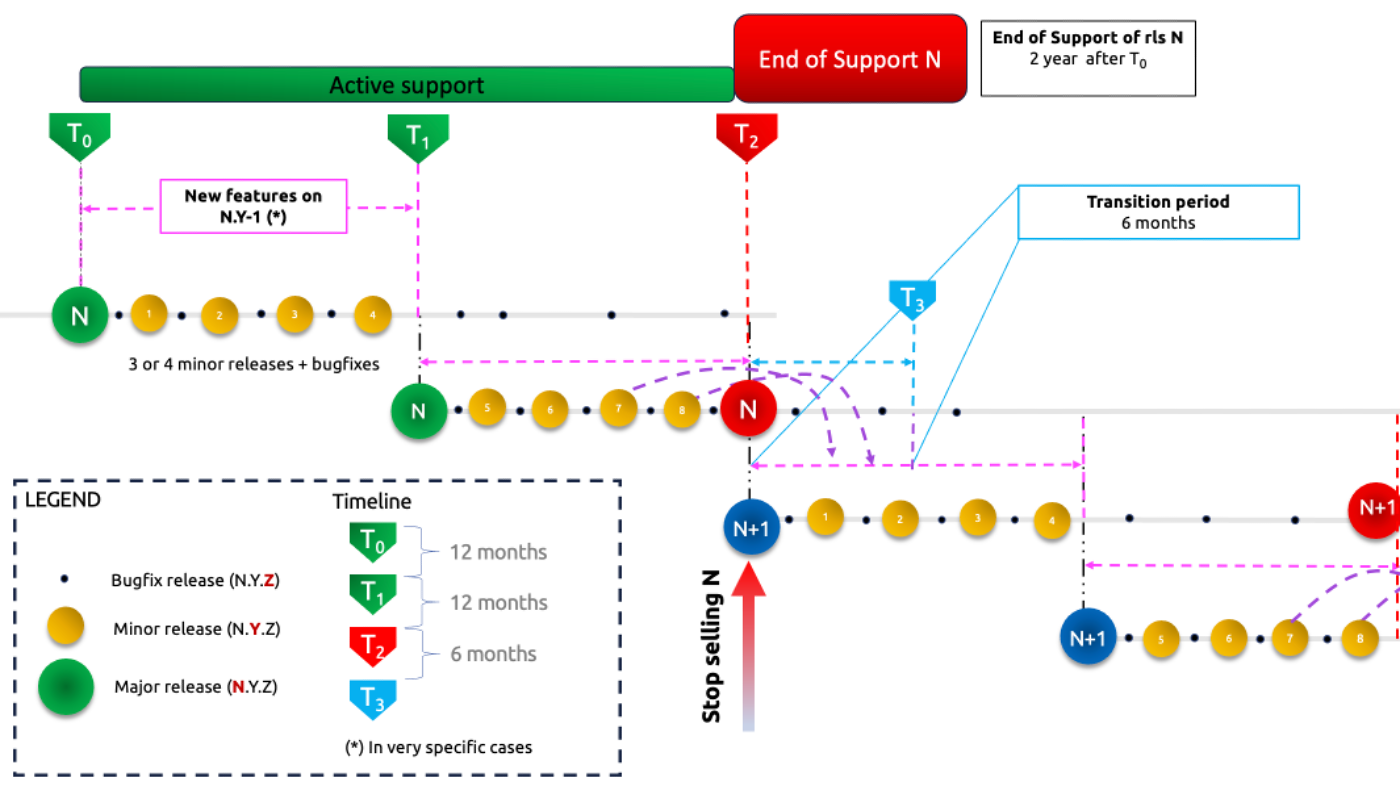
The API Orchestration (APIO) solution broadly follows the same release cycle strategy as the Fusion and Fusion for BroadWorks solution.
The aspects in which APIO differs from Fusion and Fusion for BroadWorks are:
- The number of minor release that the APIO solution is able to deliver. APIO will have 3 to 4 minor release per year, where Fusion and F4B will deliver 3 minor releases.
- The fact that in some very specific cases, a new feature in the release N.Y can be back-ported to a previous minor release N.Y-1 during the active support period.
Example If a new feature is delivered in the release 2.10.0 and, for a specific reason, is also required in the 2.9.z release, then this new feature can be back-ported to this 2.9 release.
The figure below shows the release cycle strategy for the APIO solution.
NIMS & NPACT release cycle management
NIMS, and NPACT, though essential in their domains, exhibit a unique approach to release cycles due to the lower frequency of customer-driven feature demands.
Unlike some counterparts such as Fusion and APIO, the development pace for NIMS and NPACT is influenced by the relatively modest influx of customer requirements for new features. This characteristic results in less frequent and continuous development cycles for these solutions. Consequently, the release versions for NIMS and NPACT are fewer in number compared to the more actively evolving Fusion and APIO solutions.
While this may imply a slower introduction of new functionalities, it also reflects the stability and maturity of these solutions. Users can anticipate a more consolidated set of features with each release, focusing on refined capabilities and enhanced performance rather than a multitude of new additions.
Moreover, to align with industry standards and ensure consistent customer support experiences, the support period for NIMS and NPACT is synchronized with that of Fusion and APIO. This standardization establishes a unified support framework across the suite of solutions, offering users a predictable and reliable support window of two years.
In conclusion, the release cycle management for NIMS and NPACT strikes a balance between stability and innovation, catering to the specific needs of users who prioritize reliability over rapid feature turnover. This strategic approach ensures that these solutions continue to serve their purpose effectively while maintaining compatibility with evolving industry standards.
Encouragement to Update
Customers are encouraged to upgrade to the latest minor and patch releases within a given major release version. This recommendation is made to ensure that customers can benefit from bug fixes and improvements that have been implemented since the previous release. Minor releases typically include new features and enhancements, while patch releases primarily focus on addressing bugs and security vulnerabilities. By staying up-to-date with these updates, customers can ensure that their software remains stable, secure, and optimized for performance. Additionally, it helps maintain compatibility with other systems and software components.
Communication and Transparency
Throughout the release cycle, Netaxis maintains transparent communication with its user base. Release notes, documentation updates, and communication channels are used to inform customers about the changes, enhancements, and bug fixes introduced for the different solutions.
In conclusion, Netaxis' release cycle management is designed to provide comprehensive support, proactive maintenance, and continuous improvement. This approach ensures that users experience a reliable and evolving software platform while allowing for a smooth transition from active to extended support periods.
Release support milestones
Fusion for BroadWorks
The table below summarizes the End of Support dates for the different Fusion for BroadWorks releases.
| Solution | Release | GA Date | End of Support date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 2.4 | 13 December 2021 | 13 December 2023 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 2.5 | 19 July 2022 | 13 December 2023 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.0 | 16 December 2022 | 15 December 2024 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.1 | 27 April 2023 | 15 December 2024 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.2 | 10 August 2023 | 15 December 2024 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.3 | 04 December 2023 | 15 December 2024 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.4 | 17 June 2024 | 31 July 2025 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.5 | 15 October 2024 | 31 January 2026 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 3.6 | 17 January 2025 | 31 January 2026 |
| Fusion for BroadWorks | 4.1 | 8 August 2025 | 31 July 2026 |
Fusion
The table below summarizes the End of Support dates for the different Fusion releases.
| Solution | Release | GA Date | End of Support date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion | 1.0 | 15 November 2022 | 15 November 2024 |
| Fusion | 1.1 | 15 January 2023 | 15 November 2024 |
| Fusion | 1.2 | 30 June 2023 | 15 November 2024 |
| Fusion | 1.3 | 31 August 2023 | 15 November 2024 |
| Fusion | 1.4 | 15 March 2024 | 15 November 2024 |
API Orchestrator (APIO)
The table below summarizes the End of Support dates for the different APIO releases.
| Solution | Release | GA Date | End of Support date |
|---|---|---|---|
| APIO Core | 0.19.4 | 23 August 2021 | 23 August 2023 |
| APIO Core | 0.20.O | 12 October 2021 | 23 August 2023 |
| APIO Core | 0.21.0 | 06 December 2021 | 23 August 2023 |
| APIO Core | 0.22.0 | 30 March 2022 | 23 August 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.0 | 12 October 2021 | 12 October 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.1 | 09 December 2021 | 12 October 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.2 | 20 April 2022 | 12 October 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.3 | 25 August 2022 | 12 October 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.4 | 19 September 2022 | 12 October 2023 |
| APIO Core | 2.5 | 14 October 2022 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.6 | 05 December 2022 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.7 | 09 January 2023 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.8 | 16 January 2023 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.9 | 21 February 2023 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.10 | 07 April 2023 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.11 | 17 May 2023 | 14 October 2024 |
| APIO Core | 2.12 | 12 January 2024 | 12 January 2026 |
| APIO Core | 2.13 | 11 April 2024 | 11 April 2026 |
| APIO Core | 2.14 | 08 July 2024 | 08 July 2026 |
| APIO Core | 2.15 | 08 November 2024 | 08 November 2026 |
| APIO Core | 2.16 | 02 June 2025 | 02 June 2027 |
NIMS
The table below summarizes the End of Support dates for the different NIMS releases.
| Solution | Release | GA Date | End of Support date |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIMS | 1.1.1 | 02 November 2020 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.2.1 | 10 December 2020 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.1 | 02 April 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.2 | 02 April 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.3 | 08 April 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.4 | 04 May 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.5 | 28 May 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.6 | 16 July 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.7 | 15 September 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.8 | 26 November 2021 | 02 November 2022 |
| NIMS | 1.3.9 | 11 February 2022 | 11 February 2024 |
| NIMS | 1.3.10 | 25 February 2022 | 11 February 2024 |
| NIMS | 1.3.11 | 25 February 2022 | 11 February 2024 |
| NIMS | 1.3.12 | 14 March 2022 | 11 February 2024 |
| NIMS | 1.3.13 | 14 April 2022 | 11 February 2024 |
| NIMS | 1.3.14 | 08 March 2023 | 08 March 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.3.15 | 23 March 2023 | 08 March 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.4.1 | 04 December 2023 | 04 December 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.4.2 | 07 December 2023 | 04 December 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.4.3 | 12 December 2023 | 04 December 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.4.4 | 14 December 2023 | 04 December 2025 |
| NIMS | 1.4.5 | 19 February 2024 | 04 December 2025 |
NPACT
The table below summarizes the End of Support dates for the different NPACT releases. All the versions before the release 0.8.0 are already End of Support.
| Solution | Release | GA Date | End of Support date |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPACT | 0.1.0 | 21 October 2020 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.1.1 | 09 November 2020 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.1.2 | 11 November 2020 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.1.3 | 12 November 2020 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.2.0 | 01 December 2020 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.2.1 | 25 January 2021 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.3.0 | 01 March 2021 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.4.0 | 26 March 2021 | 21 October 2022 |
| NPACT | 0.5.0 | 05 May 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.6.0 | 21 May 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.6.1 | 25 May 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.6.2 | 07 June 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.7.0 | 24 August 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.8.0 | 04 October 2021 | 05 May 2023 |
| NPACT | 0.9.0 | 21 February 2022 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.10.0 | 04 July 2022 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.11.0 | 16 August 2022 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.12.0 | 17 November 2022 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.13.0 | 25 November 2022 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.14.0 | 13 January 2023 | 21 February 2024 |
| NPACT | 0.15.0 | 26 January 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.1 | 03 February 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.2 | 09 March 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.3 | 20 June 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.4 | 02 August 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.5 | 23 August 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.6 | 14 September 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.7 | 19 October 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.8 | 22 November 2023 | 25 January 2025 |
| NPACT | 0.15.9 | 05 February 2024 | 25 January 2025 |
